边缘检测系列3:【HED】 Holistically-Nested 边缘检测
时间:2025-07-18 作者:游乐小编
本文介绍经典论文《Holistically-Nested Edge Detection》中的HED模型,这是多尺度端到端边缘检测模型。给出其Paddle实现,包括HEDBlock构建、HED_Caffe模型(对齐Caffe预训练模型)及精简HED模型,还涉及预训练模型加载、预处理、后处理操作及推理过程。

引入
除了传统的边缘检测算法,当然也有基于深度学习的边缘检测模型
这次就介绍一篇比较经典的论文 Holistically-Nested Edge Detection
其中的 Holistically-Nested 表示此模型是一个多尺度的端到端边缘检测模型
相关资料
论文:Holistically-Nested Edge Detection
最新代码(Caffe):s9xie/hed
非最新实现(Pytorch): xwjabc/hed
效果演示
论文中的效果对比图:

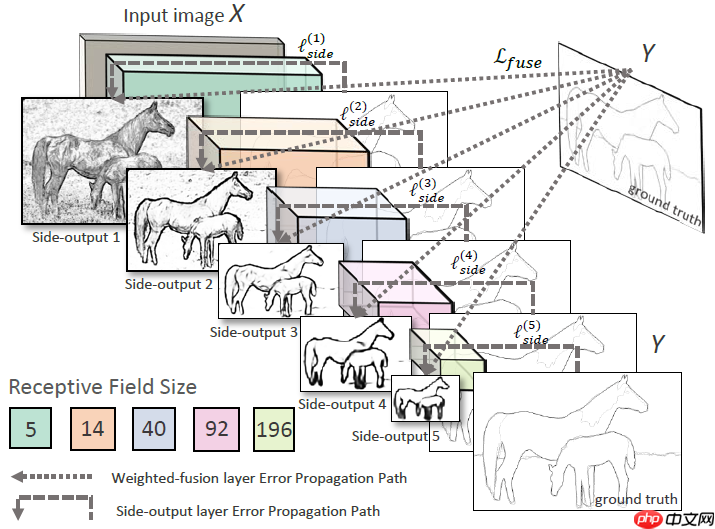
模型结构
HED 模型包含五个层级的特征提取架构,每个层级中:
使用 VGG Block 提取层级特征图
使用层级特征图计算层级输出
层级输出上采样
最后融合五个层级输出作为模型的最终输出:
通道维度拼接五个层级的输出
1x1 卷积对层级输出进行融合
模型总体架构图如下:
代码实现
导入必要的模块
In [1]import cv2import numpy as npfrom PIL import Imageimport paddleimport paddle.nn as nn登录后复制
构建 HED Block
由一个 VGG Block 和一个 score Conv2D 层组成
使用 VGG Block 提取图像特征信息
使用一个额外的 Conv2D 计算边缘得分
In [2]class HEDBlock(nn.Layer): def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, paddings, num_convs, with_pool=True): super().__init__() # VGG Block if with_pool: pool = nn.MaxPool2D(kernel_size=2, stride=2) self.add_sublayer('pool', pool) conv1 = nn.Conv2D(in_channels=in_channels, out_channels=out_channels, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=paddings[0]) relu = nn.ReLU() self.add_sublayer('conv1', conv1) self.add_sublayer('relu1', relu) for _ in range(num_convs-1): conv = nn.Conv2D(in_channels=out_channels, out_channels=out_channels, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=paddings[_+1]) self.add_sublayer(f'conv{_+2}', conv) self.add_sublayer(f'relu{_+2}', relu) self.layer_names = [name for name in self._sub_layers.keys()] # Socre Layer self.score = nn.Conv2D(in_channels=out_channels, out_channels=1, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0) def forward(self, input): for name in self.layer_names: input = self._sub_layers[name](input) return input, self.score(input)登录后复制构建 HED Caffe 模型
本模型基于最新开源的 Caffe 预训练模型实现,预测结果非常接近最新实现。
此代码会稍显冗余,主要是为了对齐最新提供的预训练模型,具体的原因请参考如下说明:
由于 Paddle 的 Bilinear Upsampling 与 Caffe 的 Bilinear DeConvolution 并不完全等价,所以这里使用 Transpose Convolution with Bilinear 进行替代以对齐模型输出。
因为最新开源的 Caffe 预训练模型中第一个 Conv 层的 padding 参数为 35,所以需要在前向计算时进行中心裁剪特征图以恢复其原始形状。
裁切所需要的参数参考自 XWJABC 的复现代码,代码链接
In [3]class HED_Caffe(nn.Layer): def __init__(self, channels=[3, 64, 128, 256, 512, 512], nums_convs=[2, 2, 3, 3, 3], paddings=[[35, 1], [1, 1], [1, 1, 1], [1, 1, 1], [1, 1, 1]], crops=[34, 35, 36, 38, 42], with_pools=[False, True, True, True, True]): super().__init__() ''' Caffe HED model re-implementation in Paddle. This model is based on the official Caffe pre-training model. The inference results of this model are very close to the official implementation in Caffe. Pytorch and Paddle's Bilinear Upsampling are not completely equivalent to Caffe's DeConvolution with Bilinear, so Transpose Convolution with Bilinear is used instead. In the official Caffe pre-training model, the padding parameter value of the first convolution layer is equal to 35, so the feature map needs to be cropped. The crop parameters refer to the code implementation by XWJABC. The code link: https://github.com/xwjabc/hed/blob/master/networks.py#L55. ''' assert (len(channels) - 1) == len(nums_convs), '(len(channels) -1) != len(nums_convs).' self.crops = crops # HED Blocks for index, num_convs in enumerate(nums_convs): block = HEDBlock(in_channels=channels[index], out_channels=channels[index+1], paddings=paddings[index], num_convs=num_convs, with_pool=with_pools[index]) self.add_sublayer(f'block{index+1}', block) self.layer_names = [name for name in self._sub_layers.keys()] # Upsamples for index in range(2, len(nums_convs)+1): upsample = nn.Conv2DTranspose(in_channels=1, out_channels=1, kernel_size=2**index, stride=2**(index-1), bias_attr=False) upsample.weight.set_value(self.bilinear_kernel(1, 1, 2**index)) upsample.weight.stop_gradient = True self.add_sublayer(f'upsample{index}', upsample) # Output Layers self.out = nn.Conv2D(in_channels=len(nums_convs), out_channels=1, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0) self.sigmoid = nn.Sigmoid() def forward(self, input): h, w = input.shape[2:] scores = [] for index, name in enumerate(self.layer_names): input, score = self._sub_layers[name](input) if index > 0: score = self._sub_layers[f'upsample{index+1}'](score) score = score[:, :, self.crops[index]: self.crops[index] + h, self.crops[index]: self.crops[index] + w] scores.append(score) output = self.out(paddle.concat(scores, 1)) return self.sigmoid(output) @staticmethod def bilinear_kernel(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size): ''' return a bilinear filter tensor ''' factor = (kernel_size + 1) // 2 if kernel_size % 2 == 1: center = factor - 1 else: center = factor - 0.5 og = np.ogrid[:kernel_size, :kernel_size] filt = (1 - abs(og[0] - center) / factor) * (1 - abs(og[1] - center) / factor) weight = np.zeros((in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, kernel_size), dtype='float32') weight[range(in_channels), range(out_channels), :, :] = filt return paddle.to_tensor(weight, dtype='float32')登录后复制构建 HED 模型
下面就是一个比较精简的 HED 模型实现
与此同时也意味着下面这个模型会与最新实现的模型有所差异,具体差异如下:
3 x 3 卷积采用 padding == 1
采用 Bilinear Upsampling 进行上采样
同样可以加载预训练模型,不过精度可能会略有下降
In [4]# class HEDBlock(nn.Layer):# def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, num_convs, with_pool=True):# super().__init__()# # VGG Block# if with_pool:# pool = nn.MaxPool2D(kernel_size=2, stride=2)# self.add_sublayer('pool', pool)# conv1 = nn.Conv2D(in_channels=in_channels, out_channels=out_channels, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1)# relu = nn.ReLU()# self.add_sublayer('conv1', conv1)# self.add_sublayer('relu1', relu)# for _ in range(num_convs-1):# conv = nn.Conv2D(in_channels=out_channels, out_channels=out_channels, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1)# self.add_sublayer(f'conv{_+2}', conv)# self.add_sublayer(f'relu{_+2}', relu)# self.layer_names = [name for name in self._sub_layers.keys()]# # Socre Layer# self.score = nn.Conv2D(# in_channels=out_channels, out_channels=1, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0)# def forward(self, input):# for name in self.layer_names:# input = self._sub_layers[name](input)# return input, self.score(input)# class HED(nn.Layer):# def __init__(self,# channels=[3, 64, 128, 256, 512, 512],# nums_convs=[2, 2, 3, 3, 3],# with_pools=[False, True, True, True, True]):# super().__init__()# '''# HED model implementation in Paddle.# Fix the padding parameter and use simple Bilinear Upsampling.# '''# assert (len(channels) - 1) == len(nums_convs), '(len(channels) -1) != len(nums_convs).'# # HED Blocks# for index, num_convs in enumerate(nums_convs):# block = HEDBlock(in_channels=channels[index], out_channels=channels[index+1], num_convs=num_convs, with_pool=with_pools[index])# self.add_sublayer(f'block{index+1}', block)# self.layer_names = [name for name in self._sub_layers.keys()]# # Output Layers# self.out = nn.Conv2D(in_channels=len(nums_convs), out_channels=1, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0)# self.sigmoid = nn.Sigmoid()# def forward(self, input):# h, w = input.shape[2:]# scores = []# for index, name in enumerate(self.layer_names):# input, score = self._sub_layers[name](input)# if index > 0:# score = nn.functional.upsample(score, size=[h, w], mode='bilinear')# scores.append(score)# output = self.out(paddle.concat(scores, 1))# return self.sigmoid(output)登录后复制预训练模型
In [5]def hed_caffe(pretrained=True, **kwargs): model = HED_Caffe(**kwargs) if pretrained: pdparams = paddle.load('hed_pretrained_bsds.pdparams') model.set_dict(pdparams) return model登录后复制预处理操作
类型转换
归一化
转置
增加维度
转换为 Paddle Tensor
In [6]def preprocess(img): img = img.astype('float32') img -= np.asarray([104.00698793, 116.66876762, 122.67891434], dtype='float32') img = img.transpose(2, 0, 1) img = img[None, ...] return paddle.to_tensor(img, dtype='float32')登录后复制后处理操作
上下阈值限制
删除通道维度
反归一化
类型转换
转换为 Numpy NdArary
In [7]def postprocess(outputs): results = paddle.clip(outputs, 0, 1) results = paddle.squeeze(results, 1) results *= 255.0 results = results.cast('uint8') return results.numpy()登录后复制模型推理
In [8]model = hed_caffe(pretrained=True)img = cv2.imread('sample.png')img_tensor = preprocess(img)outputs = model(img_tensor)results = postprocess(outputs)show_img = np.concatenate([cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB), cv2.cvtColor(results[0], cv2.COLOR_GRAY2RGB)], 1)Image.fromarray(show_img)登录后复制登录后复制代码解释
小编推荐:
相关攻略
更多 热门推荐
更多 热门文章
更多 -
- 神角技巧试炼岛高级宝箱在什么位置
-
2021-11-05 11:52
手游攻略
-

- 王者荣耀音乐扭蛋机活动内容奖励详解
-
2021-11-19 18:38
手游攻略
-
- 坎公骑冠剑11
-
2021-10-31 23:18
手游攻略
-

- 原神卡肉是什么意思
-
2022-06-03 14:46
游戏资讯
-

- 《臭作》之100%全完整攻略
-
2025-06-28 12:37
单机攻略
























